

Recognition of Energy Savings from a Factory Heating and Cooling System Using an Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage System
- Focus on the unutilized energy of 700kw in geothermal heat, with cyclical use of heat throughout the year for effective energy utilization.
- Reduction in heat emissions into the atmosphere, and underground heat balance of zero for the full year period, also helps to protect the global environment.
TOKYO, Dec 23, 2021 - (JCN Newswire) - Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Thermal Systems, Ltd. (MHI Thermal Systems), a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group, has won the Energy Conservation Center, Japan Chairman's Award in "Best Practice Category" at the 2021 Energy Conservation Grand Prize sponsored by the Energy Conservation Center, Japan (ECCJ), with support from Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). This award was presented for measures relating to energy savings from a factory heating and cooling system utilizing an aquifer(1) thermal energy storage (ATES) system. The use of underground water stored in aquifers as a source of heat for heating and cooling systems is highly regarded for its energy conservation potential, environmental performance, and other benefits. This is the first time MHI Thermal Systems has received an award in Best Practices Category.
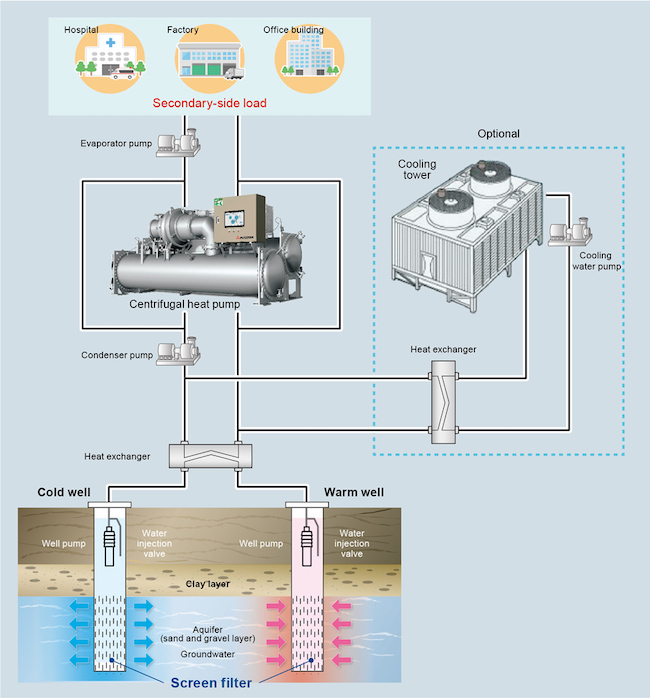 |
The initiative recognized with this reward is the introduction of an ATES system that takes advantage of the unutilized energy of 700kw in geothermal heat for the heating and cooling system at the MHI Thermal Systems Kobe Works, located on the grounds of the MHI Kobe Shipyard & Machinery Works in Hyogo Prefecture. This system provides efficient use of energy by allowing for the cyclical use of heat across seasons, utilizing the cold exhaust from heating during the wintertime for air conditioning during the summer, and warm exhaust from air conditioning during the summertime for heating during the winter. In addition, the reduction in heat emissions into the atmosphere, an underground heat balance of zero for the full year period, and other benefits, contribute to cutting CO2 emissions, alleviating the heat island effect, and preventing global warming.
Additional energy-saving measures adopted for the ATES system include the use of a high-performance inverter centrifugal heat pump(2) with low-GWP(3) refrigerant, adoption of an optimal control system, introduction of visualization systems to assess energy usage and heat source well performance, and utilization of initial year operating data for long-term operation from the second year and beyond. As a result, compared to a gas absorption cold/hot water heater with similar capacity, this system provides a reduction in annual primary energy consumption equivalent to 46.5kL in crude oil per annum (reduction rate of 49.9%), and CO2 reductions of 109.1 tonnes per annum (reduction rate of 65.3%).
The ECCJ Energy Conservation Grand Prize were established in 2011 to raise awareness of energy conservation, promote related activities and initiatives, and contribute to the widespread adoption of energy-efficient products and practices. The annual awards program recognizes outstanding energy-saving initiatives at businesses or workplaces that serve as examples for other companies, or outstanding energy-saving products and business models.
MHI Thermal Systems, encouraged by this award, will continue to develop technologies and products that further contribute to energy conservation. In addition, by drawing on the collective technological capabilities realized through synergies generated from its wide-ranging business domain, including the thermal engineering business to enhance energy efficiency in many types of production plants, the large-scale refrigerator business for cooling large spaces, and the air conditioning business to create a wide range of comfortable spaces, as well as the transport refrigerating systems business essential to cold chains, and the automotive air-conditioning business, MHI Thermal Systems will focus on achieving optimal thermal solutions to meet the varied needs of customers.
(1) An aquifer is an underground layer composed of gravel or other materials. Because the groundwater stored in this layer is cooler than the ambient temperature in summer and warmer in winter, it is considered unutilized temperature difference energy with high utility value as a heat source.
(2) The use of warm water specifications based on the ETI-Z Series of centrifugal chillers for air conditioners manufactured by MHI Thermal Systems allows for switching between heating and cooling modes. See the following press release for more information on the ETI-Z Series.
https://www.mhi.com/news/1506101900.html
(3) Global Warming Potential (GWP) is a coefficient, with CO2 fixed at a GWP of 1.0. Smaller values indicate greater environmental performance.
Source: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Copyright 2021 JCN Newswire . All rights reserved.
© 2021 JCN Newswire
