Resource Expansion Potential at Valley: Hole V-24-115 intersects 2.08 g/t Au over 15.5 m within a broader 100.5 m intersection averaging 0.53 g/t Au, showing strong mineralization in an unexplored part of the Valley intrusion over 300 m east of the Valley deposit, Rogue Project
Continuity Confirmed: Hole V-24-117 intersects 1.64 g/t Au over 112.5 m within a broader 242.5 m intersection averaging 1.14 g/t Au, demonstrating strong continuity of the Valley Deposit
District Potential Demonstrated: Einarson Project hole J-24-031 returns 20.94 g/t Au over 2.1 m within 9.45 m of 6.81 g/t Au at the Jupiter target, expanding mineralization 50 m to depth (open) and advancing understanding of structural controls
Drilling Update: Assays remain pending for >2,500 m from 6 holes from infill and expansionary drilling at Snowline's Valley deposit, Rogue Project.
VANCOUVER, BC / ACCESS Newswire / February 19, 2025 / SNOWLINE GOLD CORP (TSX-V:SGD)(OTCQB:SNWGF) (the "Company" or "Snowline") is pleased to announce further results from its 2024 drill campaign on the Valley deposit, Rogue Project, and from its Jupiter target on the adjacent Einarson Project, Yukon. At Valley, holes V-24-114 and V-24-115 both returned intervals of strong gold mineralization outside of the existing MRE, demonstrating the presence of gold within a large and still untested part of the Valley intrusion. Additional holes V-24-116 and V-24-117 show continuity of >1 g/t gold grades along multiple edges of the primary deposit area at Valley. These results will help to inform an updated MRE for Valley anticipated in the coming months. At Jupiter, roughly 30 km north of Valley on the adjacent Einarson Project, three of four reported holes intersected >8 g/t Au mineralization, with an interval of 20.9 g/t Au over 2.1 m (~true width) in J-24-031 confirming a secondary east-west structural control on mineralization that could assist with future targeting at Jupiter and regionally. Results are pending for an additional >2,500 m of drilling in six holes from infill and expansionary drilling at the Valley deposit, Rogue Project.
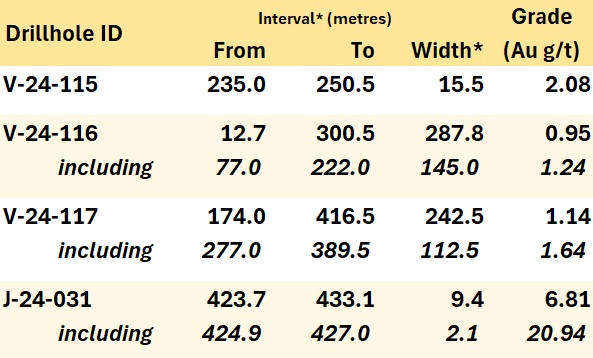
Table 1 -Highlight summary of Snowline's latest assay results; see Tables 2 (Valley) and 3 (Jupiter) for details. *Interval widths reported.
"The near-surface, high-grade part of the Valley intrusion that hosts Snowline's Valley gold deposit rightfully commands a lot of attention," said Scott Berdahl, CEO & Director of Snowline. "Today's results from other parts of the Valley intrusion and from the separate Jupiter target are both great reminders that the Valley deposit was not created in a vacuum, but rather as a product of target-scale and regional-scale geological processes underpinned by gold fertility of the eastern Selwyn Basin. Hole V-24-115 highlights the potential of the Valley intrusion itself-outside of the current Valley deposit-to host additional zones of high-grade gold mineralization. Roughly 30 km to the north, at our Jupiter target, the grades seen in J-24-031 are encouraging and further enhance our understanding of this structurally-controlled system. Both results support Snowline's founding conviction that a previously unrecognized gold district could exist within our project boundaries in the eastern Yukon Territory.
"My congratulations go to Snowline's team for the innovative, data- and observation-driven thinking that led to these drill holes and today's discoveries. We are excited to get back out into the field in 2025 as we continue to advance these ideas and others throughout our robust, district-scale project pipeline."
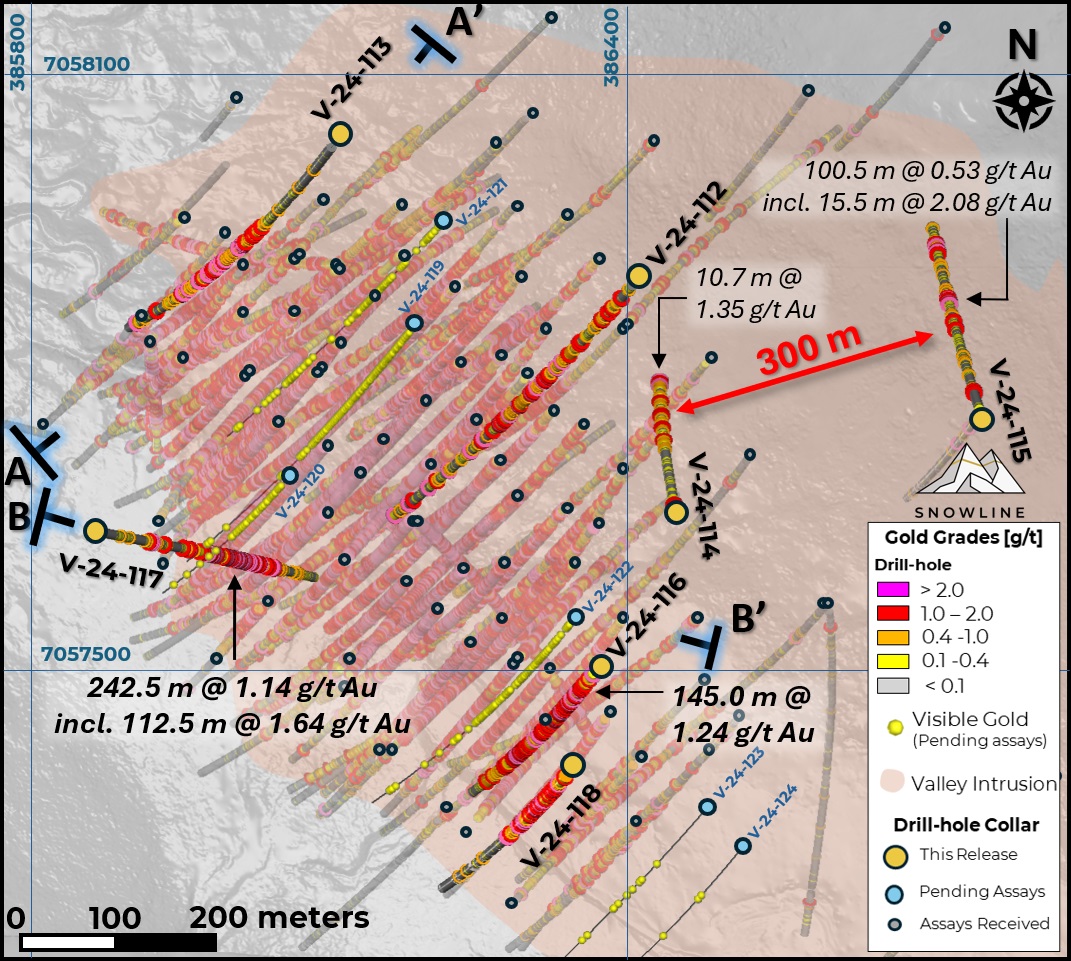
Figure 1 - Plan map of drill results and progress on the Rogue Project's Valley deposit, highlighting current results in drill holes V-24-112 through V-24-118. Past analytical results are faded, while instances of visible gold in holes awaiting assay are marked by yellow spheres. Drill holes with assays pending (6 holes from Valley) are denoted by blue collars.
VALLEY DRILLING, ROGUE PROJECT
The seven holes reported herein from Valley primarily target the margins of the known deposit as well as untested areas beyond these margins (e.g. V-24-113, 114 & 115). The results continue to build on the Company's understanding of the Valley deposit through de-risking and potential expansion.
Roughly 25,000 m were drilled at Valley in 55 holes in 2024 - nearly double the amount of drilling (27,911 m) used to inform the Company's initial MRE for Valley. The results of this drilling will be used to produce an updated MRE on the Valley deposit in Q1 or Q2 of 2025, as well as to inform future economic studies.
Hole V-24-112
Drilled as a 50 m step-out from V-22-015 along the eastern edge of the Valley deposit (Figure 1), V-24-112 intersected multiple mineralized intervals, including a 237.0 m length averaging 0.75 g/t Au from 147.5 m downhole (Table 2). This mineralization-at nearly double the 0.4 g/t Au mill cutoff grade used for the 2024 Valley MRE-expands the breadth of the company's understanding of the eastern edge of the Valley deposit.
Including non-mineralized intervals, V-24-112 averages 0.5 g/t Au over 599.9 m downhole from bedrock surface at 11.1 m.
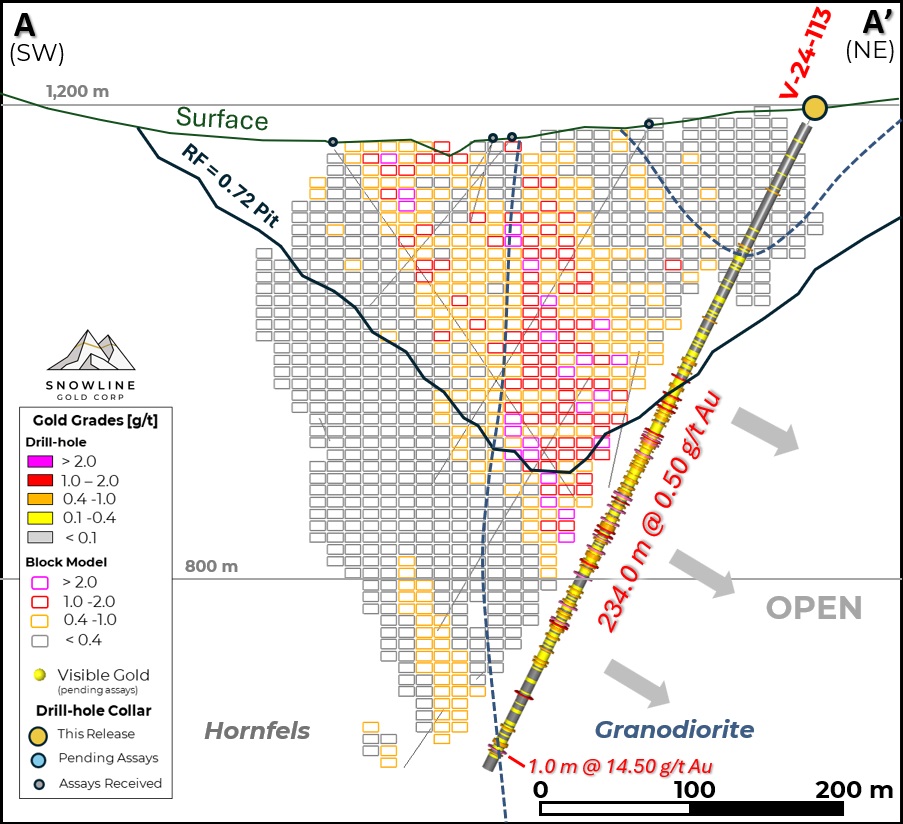
Figure 2 - Cross-section A-A', showing V-24-113 in the context of the initial Valley MRE block model and MRE-constraining revenue factor 0.72 pit shell. The block model has not been updated to reflect the current results, nor any results to date from 2024 (bold labels). Blocks shown outside of the current pit shell constraint are not included in the initial MRE for Valley. Areas without blocks have not been modelled and were assumed as nil for the initial Valley MRE.
Hole V-24-113
V-24-113 is a 140 m step back along section from V-24-097 (Figure 2) and a 60 m step to the north of V-23-038, testing mineralization at depth beyond what is currently the northeastern edge of the Valley deposit. The strongest interval of mineralization averaged 0.50 g/t Au over 234.0 m from 207.5 m downhole, with this interval occurring entirely outside the limits of the block model used to inform the 2024 MRE for Valley.
Hole V-24-114
Drilled towards the northwest, away from the eastern edge of the Valley deposit, V-24-114 encountered muted grades initially before intersecting 122.2 m averaging 0.47 g/t Au from 93.5 m downhole. Vein density and instances of visible gold increase with depth down the hole. The hole ends in mineralization, with the final 10.5 m downhole averaging 1.35 g/t Au well outside the Valley MRE, adjacent to on an open void in drill coverage (Figure 1).
Hole V-24-115
Like V-24-114, V-24-115 is also oriented northwest, drilled into a large volume of the Valley intrusion that has seen little to no drill testing (Figure 1), crosscutting an east-west oriented vein trend observed in this area. The hole hit multiple zones of mineralization, most notably a 100.5 m intersection averaging 0.53 g/t Au from 172.0 m downhole, with a 15.5 m downhole intersection averaging 2.08 g/t Au.
Notably, the drill hole primarily encountered coarse-grained granodiorite-the host phase to most of the mineralization in the Valley deposit-as opposed to a medium-grained phase expected based on previous hole V-22-017 (collared from the same site but drilled southwest). The 15.5 m interval of 2.08 g/t Au is associated with a dike of fine-grained porphyritic granodiorite, which is thought to be a causative intrusive phase for the high grades seen in the main part of the Valley deposit.
The hole ended in coarse-grained granodiorite and did not intersect the northeastern wall of the Valley intrusion, which remains unconstrained at depth.
Hole V-24-116
V-24-116 infills a 130 m gap in section between V-23-041 and V-23-042, on the southeastern side of the deposit. An interval of 287.8 m downhole averaging 0.95 g/t Au from bedrock surface at 12.7 m downhole, including 145.0 m at 1.24 g/t Au from 77.0 m downhole, confirms continuity of strong mineralization in this part of the Valley deposit.
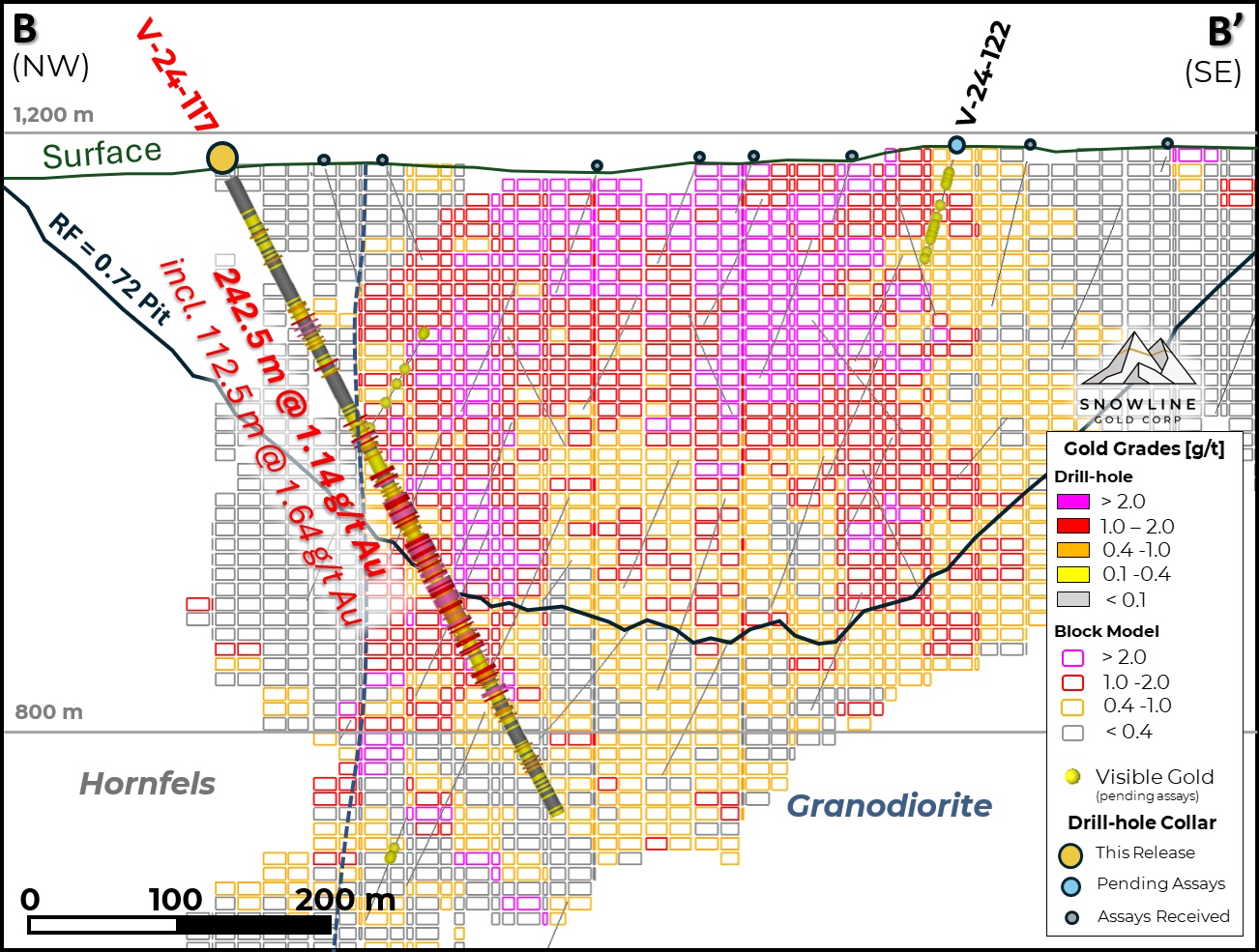
Figure 3 - Cross-section B-B', showing V-24-117 in the context of the initial Valley MRE block model and MRE-constraining revenue factor 0.72 pit shell. The block model has not been updated to reflect the current results, nor any results to date from 2024 (bold labels). Blocks shown outside of the current pit shell constraint are not included in the initial MRE for Valley. Areas without blocks have not been modelled and were assumed as nil for the initial Valley MRE. Instances of visible gold in holes still awaiting assay results are marked by yellow spheres.
Hole V-24-117
Collared outside of the Valley intrusion and drilled from west to east, V-24-117 encountered sparse zones of mineralization in the hornfels zone followed by a broad zone of mineralization on entering the Valley intrusion, returning 242.5 m at 1.14 g/t Au from 174.0 m downhole, including 112.5 m at 1.64 g/t Au from 277.0 m downhole. This interval, which spans the edge of the resource limiting pit-shell constraint for the 2024 Valley MRE, adds dimensionality to a zone of mineralization encountered at depth in previous hole V-23-039.
Hole V-24-118
V-24-118 is among the southernmost holes drilled at Valley (Figure 1). The hole averages 0.71 g/t Au over the top 221.9 m from bedrock surface at 18.6 m downhole, with the bottom 59.0 m of this interval occurring outside of the resource-limiting pit constraint used for the 2024 Valley MRE.
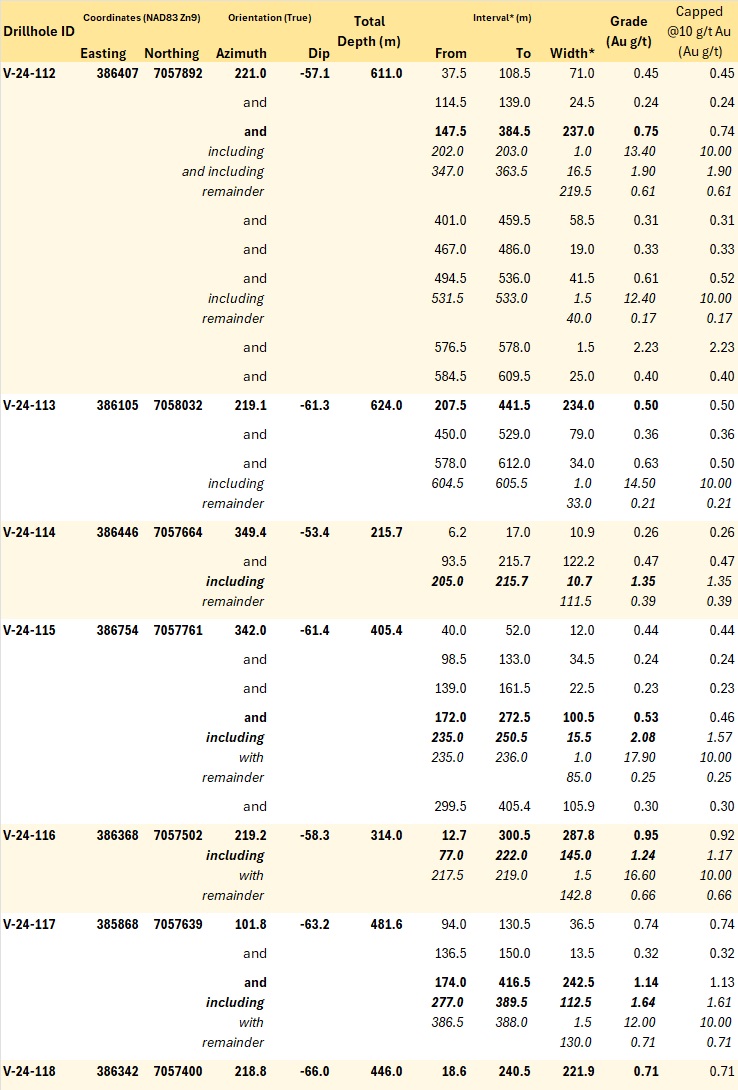
Table 2 - Summary of significant mineralization returned from current holes from Valley. The consistency of strong mineralization in the Valley deposit is reinforced by the capped values in the rightmost column, wherein any assay result >10 g/t Au is replaced by 10.0 g/t Au to calculate the average interval grades. Rounding errors may be present in interval lengths. *Interval widths reported; true widths of the Valley system are complex, with different vein generations, orientations, and grade distributions present within various intervals through the bulk tonnage gold target at Valley.
JUPITER DRILLING, EINARSON PROJECT
Jupiter is an epizonal orogenic gold discovery roughly 30 km north of Valley. The four holes reported herein from Jupiter were drilled at azimuths of roughly 330° and 300° (Table 3) to test a potential secondary structural control on mineralization: steeply-dipping, east-west oriented quartz-carbonate veins and breccias cutting at right angles to the primary controlling fold and thrust geometry. The holes successfully intersect such mineralized structures, particularly in the case of J-24-031, which returned a highlight interval of 6.81 g/t Au over 9.4 m, including 20.94 g/t Au over 2.1 m. These results expand the known footprint of high-grade gold mineralization at Jupiter by over 50 m and provide useful geological information for advancing exploration at Jupiter and on surrounding targets.
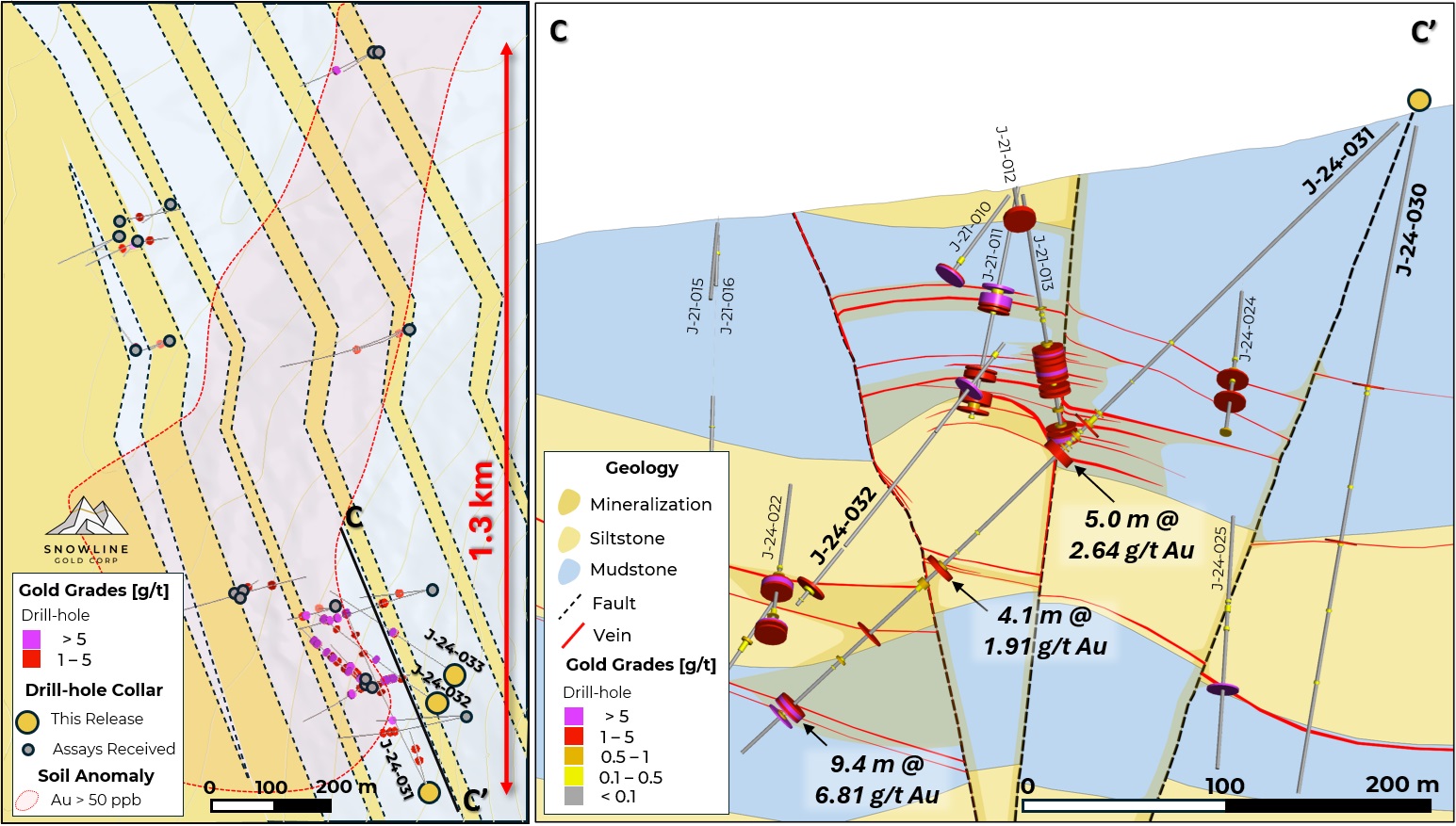
Figure 4 - Map (left) and section (right) views of the Jupiter target, showing the locations and results of J-24-030 and J-24-031 in the context of interpreted geology and surrounding drilling. To date, only a small portion of a broader 3 km soil anomaly at Jupiter has been tested by drilling, though high grades have been encountered on a footprint of >1 km strike length. Additional targets like Galatea and Avalanche Creek 5 km and 12 km to the south respectively along a prominent structural corridor, as well as the Mars target on a parallel structural corridor 4 km to the west, demonstrate widespread potential for orogenic gold mineralization on the Einarson project.
Hole J-24-031
Drillhole J-24-031 is collared in mudstone and intersects the siltstone unit marking the steep flank of a fold interference pattern at a downhole depth of 246.5 m. An interval of 31.4 m within the mudstone averages 0.68 g/t Au from 216.1 m downhole. This interval features shallow south-dipping quartz-carbonate veins and a meter-thick, east-west oriented sub-vertical quartz carbonate vein that contains visible gold (Figure 5).
Additional mineralized veins and breccia zones were encountered along the length of the hole (Table 3, Figure 4), confirming in multiple instances the steeply dipping, east-west orientations. Of note, the 9.4 m interval from 423.7 m downhole averaged 6.81 g/t Au, including a 2.1 m interval averaging 20.94 g/t Au (approximate true thickness). The strongest gold grades in this interval are seen in the country rock surrounding a 1.4 m stylolitic vein breccia. The interval expands high grade mineralization seen in J-21-022 and J-24-032 by roughly 50 m to depth and to the east.
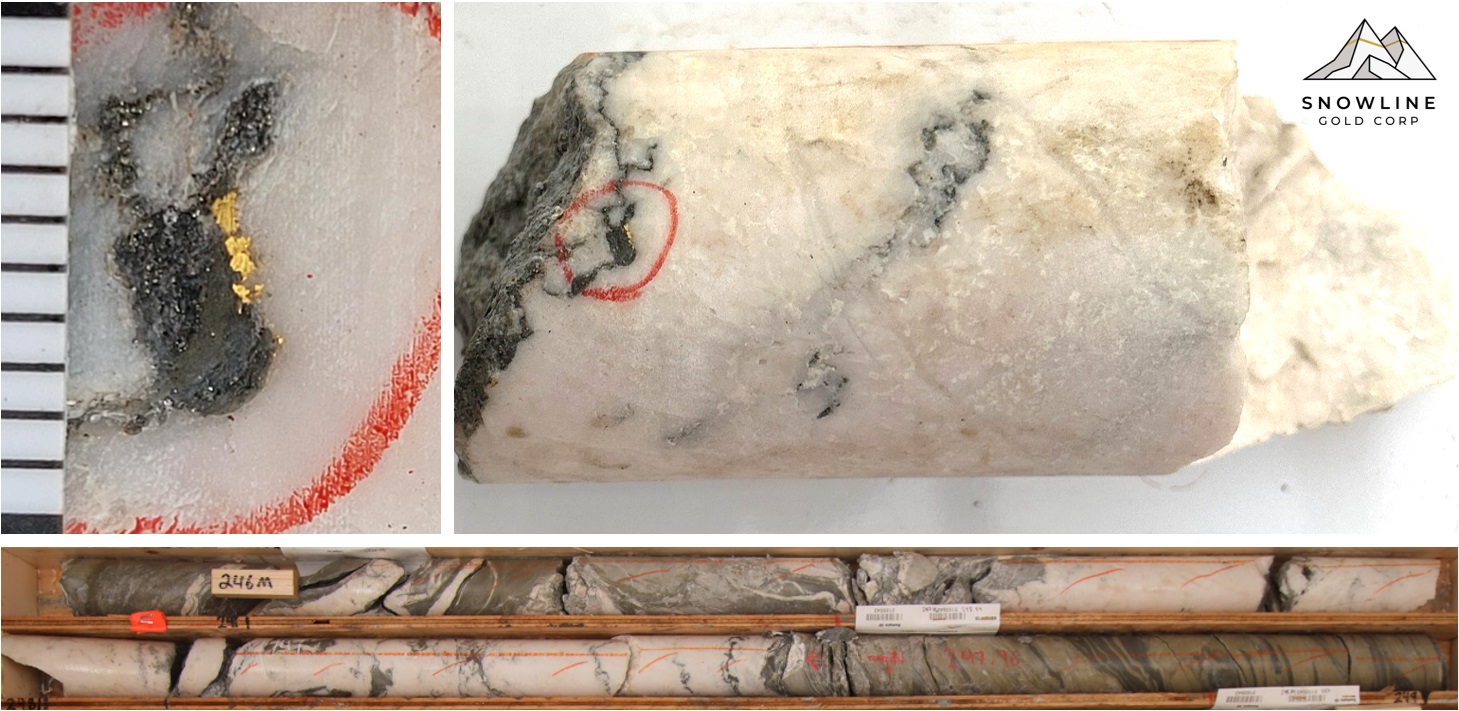

Figure 5 - Visible gold in a steeply dipping E-W quartz-carbonate vein from J-24-031 at 246.5 m downhole. The vein material averaged 4.3 g/t over 1.5 m from 246.0 m downhole, at the base of a broader zone averaging 2.64 g/t Au over 5.0 m from 242.5 m downhole. Core diameter is 5.1 cm, with millimetres denotes by the scale bar in the top left image.
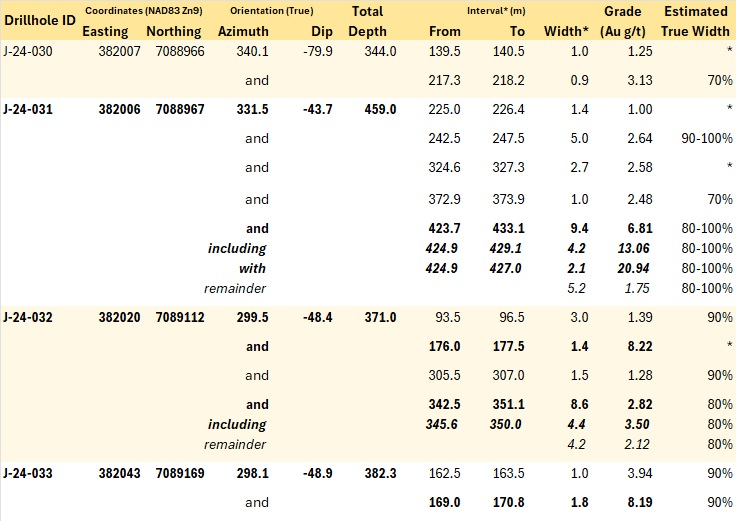
Table 3 - Summary of significant mineralization from current holes at the Jupiter target, Einarson Project. *True width of interval uncertain.
QA/QC
On receipt from the drill site NQ2-sized drill core was systematically logged for geological attributes, photographed and sampled at Snowline's "Forks" Camp. Sample lengths as small as 0.5 m were used to isolate features of interest, but most samples within moderate to strong mineralization were 1.0 m in length; otherwise, a default 1.5 m downhole sample length was used. Core was cut in half lengthwise along a pre-determined line, with one half (same half, consistently, dictated by orientation line where present or by dominant vein orientation where absent) collected for analysis and one half stored as a record. Field duplicates were collected at regular intervals as ¼ core samples by splitting the ½ core sent for sampling, leaving a consistent record of half core material from duplicate and non-duplicate samples alike. Standard reference materials and blanks were inserted by Snowline personnel at regular intervals into the sample stream. Bagged samples were sealed with security tags to ensure integrity during transport. They were delivered by expeditor to Bureau Veritas' preparatory facility in Whitehorse, Yukon. Sample preparation was completed in Whitehorse, with analyses completed in Vancouver.
Bureau Veritas is accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO9001 for quality management. Samples were crushed by BV to >85% passing below 2 mm and split using a riffle splitter. 250 g splits were pulverized to >85% passing below 75 microns. A four-acid digest with an inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) finish was used for 59-element analysis on 0.25 g sample pulps (BV code: MA250). All samples were analysed for gold content by fire assay with an atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) finish on 30 g samples (BV code: FA430). Any sample returning >10 g/t Au was reanalysed by fire assay with a gravimetric finish on a 30 g sample (BV code: FA530).
For the purposes of this release, contiguous mineralized intervals at Valley are defined as runs of mineralization with no break >5.0 m assaying <0.1 g/t Au and may include any highlight subsections thereof.
ABOUT ROGUE
Snowline Gold's 100%-owned, flagship Rogue Project, in Canada's Yukon Territory, covers a 60 x 30 km cluster of intrusions in the eastern Tombstone Gold Belt known as the Rogue Plutonic Complex.
Since its launch in 2021, Snowline has progressed the Rogue Project's Valley deposit from a greenfield prospecting discovery to a significant bulk tonnage gold resource, with 4.05 Moz gold Indicated mineral resource at 1.66 g/t Au and an additional 3.26 Moz Inferred mineral resource at 1.25 g/t Au within a pit-shell constraint. The resource estimate numbers are supported by the recent technical report for Rogue, prepared in accordance with NI 43-101 standards, entitled "Rogue Gold Project: NI 43-101 Technical Report and Mineral Resource Estimate," authored by Heather Burrell, P. Geo., Daniel J. Redmond, P. Geo., and Steven C. Haggarty, P. Eng., with an effective date of May 15, 2024.
Exploration of the open Valley deposit is ongoing. Valley is a reduced intrusion-related gold system (RIRGS), geologically similar to multi-million-ounce RIRGS deposits currently in production, like Kinross's Fort Knox Mine in Alaska, but with substantially higher gold grades. Gold is associated with bismuthinite and telluride minerals hosted in sheeted quartz vein arrays within and along the margins of a one-kilometer-scale, mid-Cretaceous aged Mayo-series intrusion.
The Rogue Project area hosts multiple intrusions similar to Valley along with widespread gold anomalism in stream sediment, soil and rock samples. Elsewhere, RIRGS deposits are known to occur in clusters. For these reasons, Snowline considers the Rogue Project to have district-scale potential to host additional reduced intrusion-related gold systems.
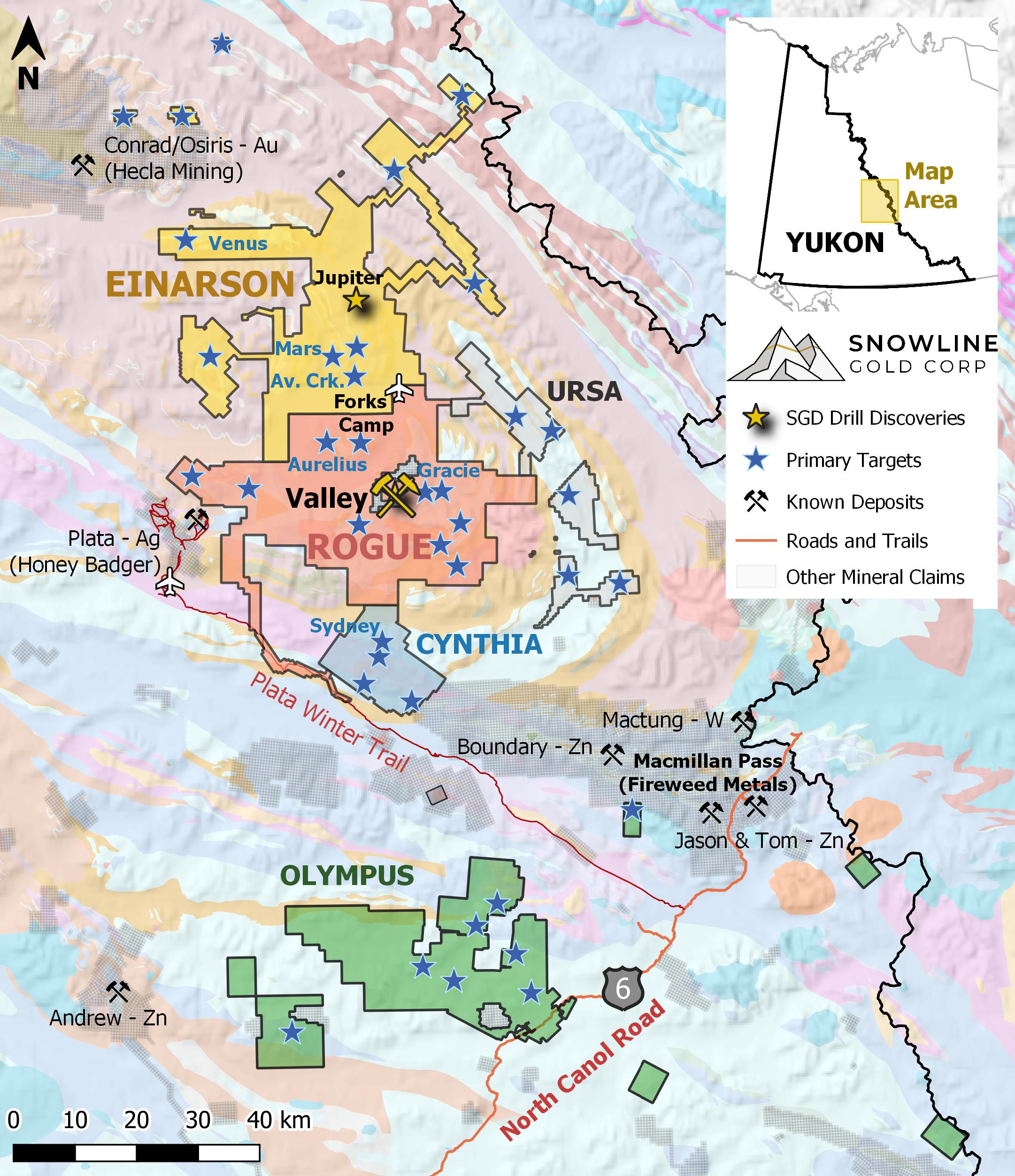
Figure 6 - Project location map for Snowline Gold's eastern Selwyn Basin properties: Rogue, Einarson, Ursa, Cynthia and Olympus. The Valley deposit and the Aurelius target are two of several prospective reduced intrusion-related gold targets on the broader 30 x 60 km Rogue Project.
ABOUT SNOWLINE GOLD CORP.
Snowline Gold Corp. is a Yukon Territory focused gold exploration and development company with an eight-project portfolio covering roughly 360,000 ha (3,600 km2). The Company is advancing its Valley deposit-a large, low-strip, near surface, >1 g/t Au bulk tonnage gold system located in the eastern Yukon-while continuing regional exploration of surrounding targets on the Rogue Project and the broader district in the highly prospective yet underexplored Selwyn Basin.
Snowline's project portfolio sits within the prolific Tintina Gold Province, host to multiple million-ounce-plus gold mines and deposits across the central Yukon and Alaska. The Company's comprehensive first-mover position and extensive exploration database provide a distinct competitive advantage and a unique opportunity for investors to be part of multiple discoveries, the advancement of a significant gold deposit, and the creation of a new gold district.
QUALIFIED PERSON
Information in this release has been prepared under supervision of and approved by Sergio Gamonal, M.Sc., P. Geo., Chief Geologist for Snowline Gold Corp, as Qualified Person for the purposes of National Instrument 43-101.
ON BEHALF OF THE BOARD
Scott Berdahl
CEO & Director
For further information, please contact:
Snowline Gold Corp.
+1 778 650 5485
info@snowlinegold.com
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This news release contains certain forward-looking statements, including statements regarding the significance of analytical results, the significance of visual drill core observations and visible gold, the potential effects of current analytical results on future mineral resource estimates including expansion of the pit shell and de-risking of the current estimate, the discovery potential within the Valley intrusion and on other exploration targets, the potential for investors to participate in multiple future discoveries, the Rogue Project having district-scale prospectivity, the creation of a new gold district and the Company's future plans and intentions. Wherever possible, words such as "may", "will", "should", "could", "expect", "plan", "intend", "anticipate", "believe", "estimate", "predict" or "potential" or the negative or other variations of these words, or similar words or phrases, have been used to identify these forward-looking statements. These statements reflect management's current beliefs and are based on information currently available to management as at the date hereof.
Forward-looking statements involve significant risk, uncertainties and assumptions. Many factors could cause actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from the results discussed or implied in the forward-looking statements. Such factors include, among other things: risks related to uncertainties inherent in drill results and the estimation of mineral resources; and risks associated with executing the Company's plans and intentions. These factors should be considered carefully, and readers should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements. Although the forward-looking statements contained in this news release are based upon what management believes to be reasonable assumptions, the Company cannot assure readers that actual results will be consistent with these forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this news release, and the Company assumes no obligation to update or revise them to reflect new events or circumstances, except as required by law.
SOURCE: Snowline Gold Corp.
View the original press release on ACCESS Newswire